
4 Case study 4
4.1 Case study on patterns of obesity across rural and urban regions
Motivated by the work of “Rising Rural Body-Mass Index Is the Main Driver of the Global Obesity Epidemic in Adults” (2019), a case study by Wright et al. (2020) explored global patterns of obesity across different regions. The questions in their case study were related to the association between Body mass index (BMI) rates with region (rural vs urban) and countries. BMI may be considered a measurement of health, where BMI is defined as an individual’s weight divided by the individual’s height. The data used for the case study is described “Rising Rural Body-Mass Index Is the Main Driver of the Global Obesity Epidemic in Adults” (2019), where the data consisted of the following variables:
Country: Countries in the sample
Sex: Men or women. The data recorded only contained data for groups of individuals described as men or women.
Region: Type of region (rural or urban)
Year: 1985 or 2017
BMI: Averaged BMI values for the given year, sex, region, and country.
We use the data to assess if BMI rates for urban and rural differ. The data are shown in table below.
Summary of findings
Numerical and graphical summaries of the BMI under different regions are provided below:
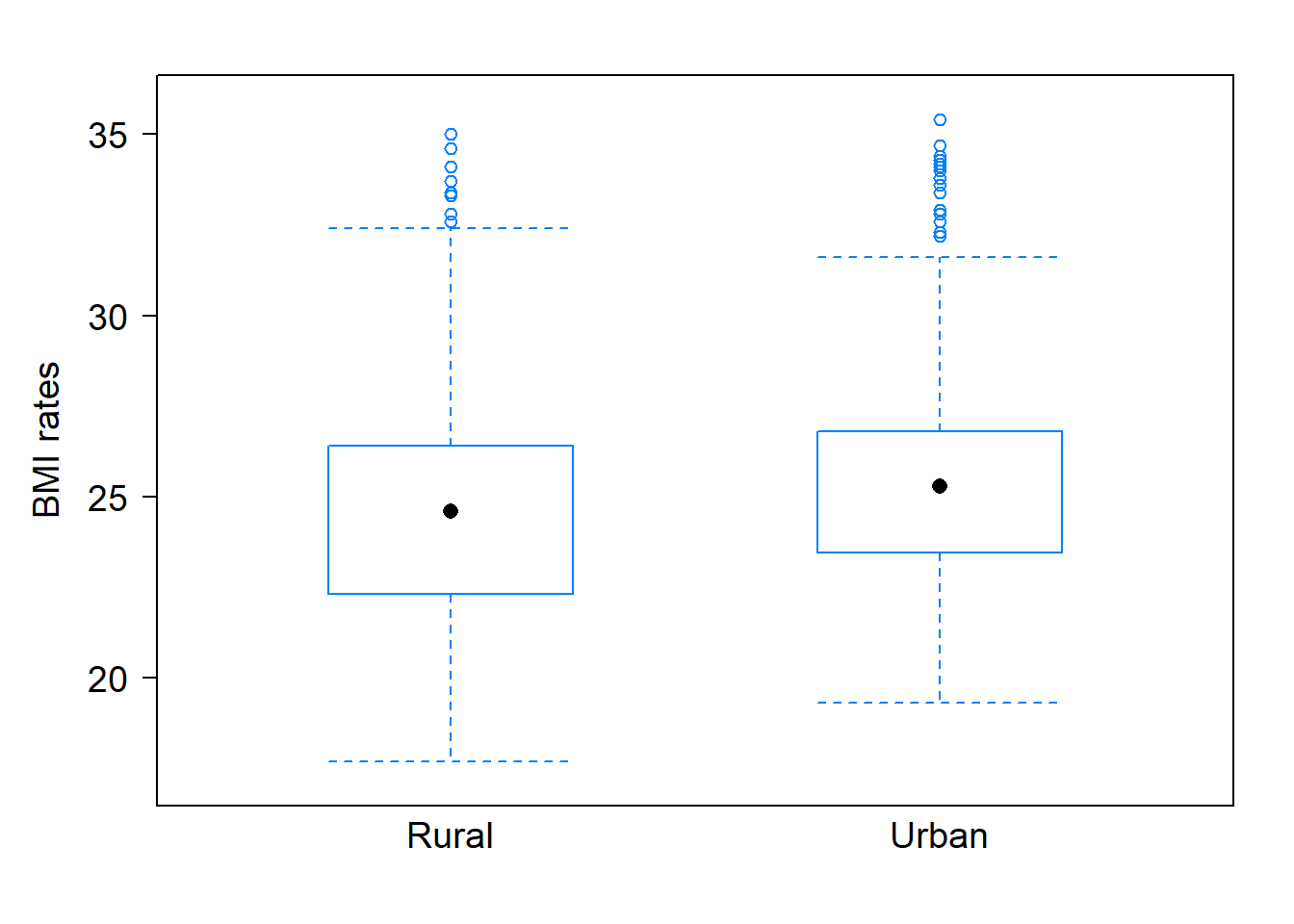
| Region | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Rural | 24.453 | 2.947 |
| Urban | 25.304 | 2.632 |
The graphical and numerical summaries show that the BMI rates for urban areas tend to be higher in the sample. However, are the samples means different enough to suggest that BMI rates are affected by region? Using statistical methods to be addressed later, the data provides convincing evidence that region affects BMI rates (p-value \(<\) 0)
Scope of inference
This case study make use of observational data, which provided convincing evidence that there is an association between BMI rates with both region and sex. The sample were not randomly selected, so these conclusions only apply to the men and women in the sampled countries.