
5 Case study 5
5.1 Case study on school shootings
School shootings occur more often in the US than any other country (Mosechkin and Krukovskiy (2019)). The K-12 School Shooting Database (Riedman (2022)) contains data on every instance a gun is brandished, is fired, or a bullet hits K-12 school property. Recently, Hilaire et al. (2022) used this data source to investigate the relationship between perpetrators’ race and how shootings are reported by the media. They found that there were differences by race in the characteristics of school shootings and media reporting of school shootings. Reeping et al. (2022) found that more permissive firearm laws and higher rates of gun ownership were associated with higher rates of school shootings. The latest raw data (Jan 1970-Nov 2022) was provided by the founder and maintainer of the K-12 School Shooting Database, David Riedman. Using this data, we explore whether the level of media coverage of the incident (Local, Regional, or National) differs across age groups and examine if the number of victims is associated with the type of weapon(s) used.
In all, the data consists of 46 variables. The variables included:
-
School_Level: education-level of the school attacked as (1) high school, (2) junior high school, (3) middle school, (4) elementary school, (5) other. -
Year: year -
Month: month -
Number_Victims: Number of victims killed or wounded -
Media_Attention: Highest level of media coverage (local, regional, or national) -
Time_Period: Time period in which the incident occurred (After school, Afternoon classes, … , Sport Event) -
agegroup: Age of the shooter (child, teen, adult) -
State: State where in incident occurred. -
Weapon_Type: The type of weapon used ()
The reader is referred to K-12 School Shooting Database data methodology page for more details regarding variables in the data set.
The data are shown in table below.
Summary of findings
Numerical and graphical summaries of the relevant variable is provided below:
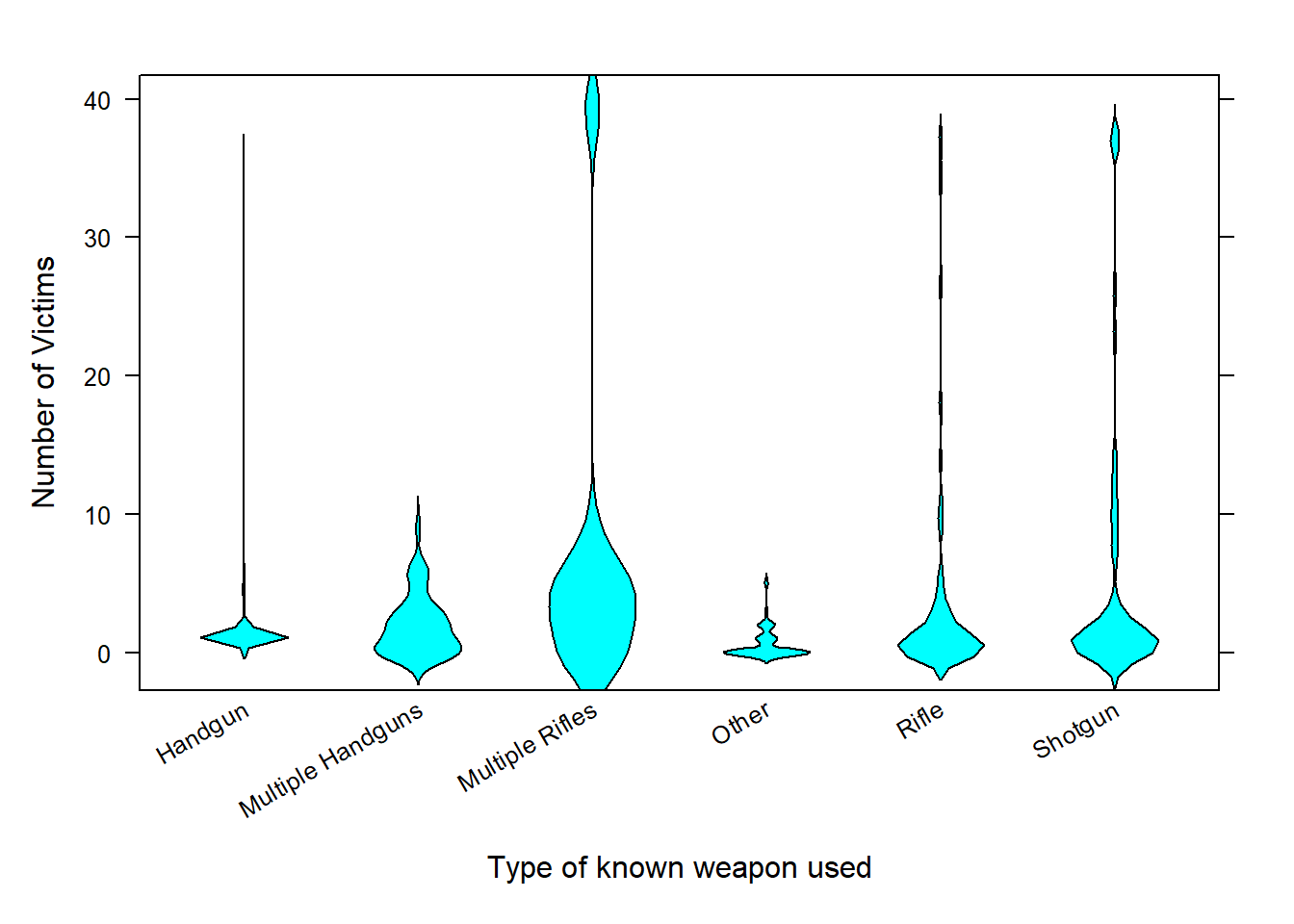
| Weapon_Type | Median | IQR |
|---|---|---|
| Handgun | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Multiple Handguns | 1.5 | 3.0 |
| Multiple Rifles | 3.5 | 5.0 |
| Other | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Rifle | 1.0 | 2.5 |
| Shotgun | 1.0 | 3.0 |
The violin boxplot shows that the number of victims differs depending on the type of weapon used, with more outlying observations under rifles or shotguns. Using statistical methods to be addressed later, the data provides very strong evidence that the number of victims varies significantly with the type of weapon used (p-value \(\approx\) 0).
Scope of inference
This case study makes use of observational data, which provided convincing evidence that there is an association between both sets of variables considered. The sample were not randomly selected, so these conclusions only apply to the sample.